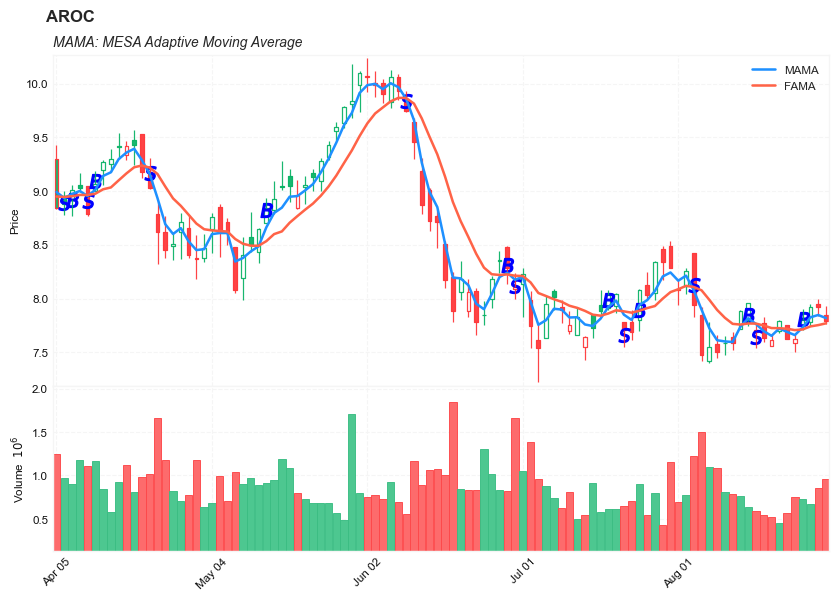
MAMA: MESA Adaptive Moving Average
Reference:
MAMA: MESA Adaptive Moving Average
The MESA Adaptive Moving Average (MAMA) adapts to price movement based on the rate change of phase as measured by the Hilbert Transform Discriminator.
The advantage of this method of adaptation is that it features a fast attack average and a slow decay average so that composite average rapidly ratchets behind price changes and holds the average value until the next ratchet occurs.
Load basic packages
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
import gc
import copy
from pathlib import Path
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, time, date
#this package is to download equity price data from yahoo finance
#the source code of this package can be found here: https://github.com/ranaroussi/yfinance/blob/main
import yfinance as yf
pd.options.display.max_rows = 100
pd.options.display.max_columns = 100
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import pytorch_lightning as pl
random_seed=1234
pl.seed_everything(random_seed)
Global seed set to 1234
1234
#S&P 500 (^GSPC), Dow Jones Industrial Average (^DJI), NASDAQ Composite (^IXIC)
#Russell 2000 (^RUT), Crude Oil Nov 21 (CL=F), Gold Dec 21 (GC=F)
#Treasury Yield 10 Years (^TNX)
#benchmark_tickers = ['^GSPC', '^DJI', '^IXIC', '^RUT', 'CL=F', 'GC=F', '^TNX']
benchmark_tickers = ['^GSPC']
tickers = benchmark_tickers + ['GSK', 'NVO', 'AROC']
#https://github.com/ranaroussi/yfinance/blob/main/yfinance/base.py
# def history(self, period="1mo", interval="1d",
# start=None, end=None, prepost=False, actions=True,
# auto_adjust=True, back_adjust=False,
# proxy=None, rounding=False, tz=None, timeout=None, **kwargs):
dfs = {}
for ticker in tickers:
cur_data = yf.Ticker(ticker)
hist = cur_data.history(period="max", start='2000-01-01')
print(datetime.now(), ticker, hist.shape, hist.index.min(), hist.index.max())
dfs[ticker] = hist
2022-08-27 13:58:24.342430 ^GSPC (5701, 7) 1999-12-31 00:00:00 2022-08-26 00:00:00
2022-08-27 13:58:24.638344 GSK (5701, 7) 1999-12-31 00:00:00 2022-08-26 00:00:00
2022-08-27 13:58:24.982461 NVO (5701, 7) 1999-12-31 00:00:00 2022-08-26 00:00:00
2022-08-27 13:58:25.208361 AROC (3782, 7) 2007-08-21 00:00:00 2022-08-26 00:00:00
ticker = 'AROC'
dfs[ticker].tail(5)
| Open | High | Low | Close | Volume | Dividends | Stock Splits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | |||||||
| 2022-08-22 | 7.59 | 7.68 | 7.50 | 7.62 | 753700 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 2022-08-23 | 7.74 | 7.90 | 7.71 | 7.80 | 732200 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 2022-08-24 | 7.78 | 7.95 | 7.74 | 7.92 | 673800 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 2022-08-25 | 7.95 | 8.00 | 7.84 | 7.92 | 857000 | 0.0 | 0 |
| 2022-08-26 | 7.85 | 7.93 | 7.76 | 7.79 | 962900 | 0.0 | 0 |
Define MAMA calculation function
def cal_mama(ohlc: pd.DataFrame, fast_limit: float = 0.5, slow_limit: float = 0.05, column: str = "close",) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""
MESA Adaptive Moving Average
The MESA Adaptive Moving Average (MAMA) adapts to price movement based on the rate change of phase as
measured by the Hilbert Transform Discriminator.
The advantage of this method of adaptation is that it features a fast attack average and a slow decay
average so that composite average rapidly ratchets behind price changes and holds the average value
until the next ratchet occurs.
source: https://www.mesasoftware.com/papers/MAMA.pdf
adapted from: https://github.com/mathiswellmann/go_ehlers_indicators/blob/bdc7bd10003c/mama.go#L110
"""
series = ohlc[column]
smooth = np.zeros(len(series))
period = np.zeros(len(series))
detrender = np.zeros(len(series))
i1 = np.zeros(len(series))
q1 = np.zeros(len(series))
ji = np.zeros(len(series))
jq = np.zeros(len(series))
i2 = np.zeros(len(series))
q2 = np.zeros(len(series))
re = np.zeros(len(series))
im = np.zeros(len(series))
smooth_period = np.zeros(len(series))
phase = np.zeros(len(series))
fama = np.zeros(len(series))
mama = np.zeros(len(series))
delta_phase = np.zeros(len(series))
alpha = np.zeros(len(series))
vals = series.values
for i in range(len(vals)):
if i<6:
mama[i] = vals[i]
fama[i] = vals[i]
continue
smooth[i] = (4*vals[i] + 3*vals[i-1] + 2*vals[i-2] + vals[i-3]) / 10
detrender[i] = (0.0962*smooth[i] + 0.5769*smooth[i-2] - 0.5769*smooth[i-4] - 0.0962*smooth[i-6]) * (0.075*period[i-1] + 0.54)
## compute InPhase and Quadrature components
q1[i] = (0.0962*detrender[i] + 0.5769*detrender[i-2] - 0.5769*detrender[i-4] - 0.0962*detrender[i-6]) * (0.075*period[i-1] + 0.54)
i1[i] = detrender[i-3]
##Advance the phase of detrender and q1 by 90 Degrees
ji[i] = (0.0962*i1[i] + 0.05769*i1[i-2] - 0.5769*i1[i-4] - 0.0962*i1[i-6]) * (0.075*period[i-1] + 0.54)
jq[i] = (0.0962*q1[i] + 0.5769*q1[i-2] - 0.5769*q1[i-4] - 0.0962*q1[i-6]) * (0.075*period[i-1] + 0.54)
##Phasor addition for 3 bar averaging
i2[i] = i1[i] - jq[i]
q2[i] = q1[i] + ji[i]
##smooth the I and Q components befor applying the discriminator
i2[i] = 0.2*i2[i] + 0.8*i2[i-1]
q2[i] = 0.2*q2[i] + 0.8*q2[i-1]
##Homodyne Discriminator
re[i] = i2[i]*i2[i-1] + q2[i]*q2[i-1]
im[i] = i2[i]*q2[i-1] - q2[i]*i2[i-1]
re[i] = 0.2*re[i] + 0.8*re[i-1]
im[i] = 0.2*im[i] + 0.8*im[i-1]
if (im[i] != 0)& (re[i] != 0):
period[i] = 360 / np.arctan(im[i]/re[i])
if (period[i] > 1.5*period[i-1]):
period[i] = 1.5 * period[i-1]
if (period[i] < 0.67*period[i-1]):
period[i] = 0.67 * period[i-1]
if (period[i] < 6):
period[i] = 6
if (period[i] > 50):
period[i] = 50
period[i] = 0.2*period[i] + 0.8*period[i-1]
smooth_period[i] = 0.33*period[i] + 0.67*smooth_period[i-1]
if (i1[i]!= 0):
phase[i] = np.arctan(q1[i] / i1[i])
delta_phase[i] = phase[i-1] - phase[i]
if (delta_phase[i] < 1):
delta_phase[i] = 1
alpha[i] = fast_limit / delta_phase[i]
if alpha[i] < slow_limit:
alpha[i] = slow_limit
mama[i] = alpha[i]*vals[i] + (1-alpha[i])*mama[i-1]
fama[i] = 0.5*alpha[i]*mama[i] + (1-0.5*alpha[i])*fama[i-1]
mama_ = pd.Series(index=series.index, data=mama, name="MAMA")
fama_ = pd.Series(index=series.index, data=fama, name="FAMA")
return pd.concat([mama_, fama_], axis=1)
def get_MAMA_signal(df):
signals = []
df.sort_index(ascending=True, inplace=True)
M_F = df['MAMA']-df['FAMA']
MAMA = df['MAMA']
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
val = 0 #not a crossing point
if M_F[i]==0:
if i<2:
val = 0
else:
if (M_F[i-1]<0):
val = 1 #from MAMA<FAMA to MAMA>FAMA
elif (M_F[i-1]>0):
val = -1 #from MAMA>FAMA to MAMA<FAMA
else:
val = 0
else:
if (i<2)|(i>=df.shape[0]-2):
val = 0
else:
if (M_F[i-1]<0) & (M_F[i]>0):
val = 2
elif (M_F[i-1]>0) & (M_F[i]<0):
val = -2
else:
val = 0
signals.append(val)
return signals
Calculate MAMA
df = dfs[ticker][['Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close', 'Volume']]
df = df.round(2)
help(cal_mama)
Help on function cal_mama in module __main__:
cal_mama(ohlc: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, fast_limit: float = 0.5, slow_limit: float = 0.05, column: str = 'close') -> pandas.core.frame.DataFrame
MESA Adaptive Moving Average
The MESA Adaptive Moving Average (MAMA) adapts to price movement based on the rate change of phase as
measured by the Hilbert Transform Discriminator.
The advantage of this method of adaptation is that it features a fast attack average and a slow decay
average so that composite average rapidly ratchets behind price changes and holds the average value
until the next ratchet occurs.
source: https://www.mesasoftware.com/papers/MAMA.pdf
adapted from: https://github.com/mathiswellmann/go_ehlers_indicators/blob/bdc7bd10003c/mama.go#L110
df_ta = cal_mama(df, column="Close")
df = df.merge(df_ta, left_index = True, right_index = True, how='inner' )
del df_ta
gc.collect()
143
signals = get_MAMA_signal(df)
df['MAMA_signal'] = signals
df['B'] = (df["MAMA_signal"]>0) .astype(int)*(df['High']+df['Low'])/2
df['S'] = (df["MAMA_signal"]<0).astype(int)*(df['High']+df['Low'])/2
display(df.head(5))
display(df.tail(5))
| Open | High | Low | Close | Volume | MAMA | FAMA | MAMA_signal | B | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | ||||||||||
| 2007-08-21 | 50.01 | 50.86 | 49.13 | 49.44 | 1029100 | 49.44 | 49.44 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007-08-22 | 48.50 | 50.70 | 47.78 | 49.29 | 996500 | 49.29 | 49.29 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007-08-23 | 49.76 | 49.82 | 47.56 | 48.03 | 742700 | 48.03 | 48.03 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007-08-24 | 47.93 | 48.77 | 47.87 | 48.58 | 416000 | 48.58 | 48.58 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007-08-27 | 48.56 | 48.81 | 46.85 | 47.47 | 447000 | 47.47 | 47.47 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Open | High | Low | Close | Volume | MAMA | FAMA | MAMA_signal | B | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | ||||||||||
| 2022-08-22 | 7.59 | 7.68 | 7.50 | 7.62 | 753700 | 7.659967 | 7.706288 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.0 |
| 2022-08-23 | 7.74 | 7.90 | 7.71 | 7.80 | 732200 | 7.729984 | 7.712212 | 2 | 7.805 | 0.0 |
| 2022-08-24 | 7.78 | 7.95 | 7.74 | 7.92 | 673800 | 7.824992 | 7.740407 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.0 |
| 2022-08-25 | 7.95 | 8.00 | 7.84 | 7.92 | 857000 | 7.846852 | 7.752653 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.0 |
| 2022-08-26 | 7.85 | 7.93 | 7.76 | 7.79 | 962900 | 7.818426 | 7.769096 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.0 |
df[['MAMA','FAMA']].hist(bins=50)
array([[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'MAMA'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'FAMA'}>]], dtype=object)
#https://github.com/matplotlib/mplfinance
#this package help visualize financial data
import mplfinance as mpf
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
# all_colors = list(mcolors.CSS4_COLORS.keys())#"CSS Colors"
all_colors = list(mcolors.TABLEAU_COLORS.keys()) # "Tableau Palette",
# all_colors = list(mcolors.BASE_COLORS.keys()) #"Base Colors",
#https://github.com/matplotlib/mplfinance/issues/181#issuecomment-667252575
#list of colors: https://matplotlib.org/stable/gallery/color/named_colors.html
#https://github.com/matplotlib/mplfinance/blob/master/examples/styles.ipynb
def plot_3panels(main_data, add_data=None, mid_panel=None, chart_type='candle', names=None,
figratio=(14,9)):
style = mpf.make_mpf_style(base_mpf_style='yahoo', #charles
base_mpl_style = 'seaborn-whitegrid',
# marketcolors=mpf.make_marketcolors(up="r", down="#0000CC",inherit=True),
gridcolor="whitesmoke",
gridstyle="--", #or None, or - for solid
gridaxis="both",
edgecolor = 'whitesmoke',
facecolor = 'white', #background color within the graph edge
figcolor = 'white', #background color outside of the graph edge
y_on_right = False,
rc = {'legend.fontsize': 'small',#or number
#'figure.figsize': (14, 9),
'axes.labelsize': 'small',
'axes.titlesize':'small',
'xtick.labelsize':'small',#'x-small', 'small','medium','large'
'ytick.labelsize':'small'
},
)
if (chart_type is None) or (chart_type not in ['ohlc', 'line', 'candle', 'hollow_and_filled']):
chart_type = 'candle'
len_dict = {'candle':2, 'ohlc':3, 'line':1, 'hollow_and_filled':2}
kwargs = dict(type=chart_type, figratio=figratio, volume=True, volume_panel=1,
panel_ratios=(4,2), tight_layout=True, style=style, returnfig=True)
if names is None:
names = {'main_title': '', 'sub_tile': ''}
added_plots = {
'S': mpf.make_addplot(add_data['S'], panel=0, color='blue', type='scatter', marker=r'${S}$' , markersize=100, secondary_y=False),
'B': mpf.make_addplot(add_data['B'], panel=0, color='blue', type='scatter', marker=r'${B}$' , markersize=100, secondary_y=False),
'MAMA': mpf.make_addplot(add_data['MAMA'], panel=0, color='dodgerblue', secondary_y=False),
'FAMA': mpf.make_addplot(add_data['FAMA'], panel=0, color='tomato', secondary_y=False),
# 'AO-SIGNAL': mpf.make_addplot(mid_panel['AO']-mid_panel['SIGNAL'], type='bar',width=0.7,panel=1, color="pink",alpha=0.65,secondary_y=False),
}
fig, axes = mpf.plot(main_data, **kwargs,
addplot=list(added_plots.values()),
)
# add a new suptitle
fig.suptitle(names['main_title'], y=1.05, fontsize=12, x=0.128)
axes[0].set_title(names['sub_tile'], fontsize=10, style='italic', loc='left')
#set legend
axes[0].legend([None]*6)
handles = axes[0].get_legend().legendHandles
# print(handles)
axes[0].legend(handles=handles[4:],labels=['MAMA', 'FAMA'])
#axes[2].set_title('AO', fontsize=10, style='italic', loc='left')
# axes[0].set_ylabel('MAMA')
# axes[0].set_ylabel(names['y_tiles'][0])
return fig, axes
start = -100
end = df.shape[0]
names = {'main_title': f'{ticker}',
'sub_tile': 'MAMA: MESA Adaptive Moving Average'}
aa_, bb_ = plot_3panels(df.iloc[start:end][['Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close', 'Volume']],
df.iloc[start:end][['B', 'S', 'MAMA', 'FAMA']],
None,
chart_type='hollow_and_filled',
names = names,
)