Pandas reshaping data with pivot pivot_table melt unstack stack
This is a Summary and Visual Explanation based on this page
References
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
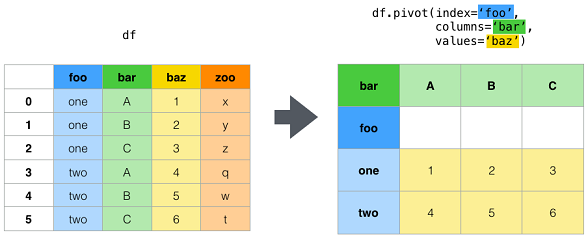
| pivot | Return reshaped DataFrame organized by given index / column values. | df.pivot(index='foo', columns='bar', values='baz') |
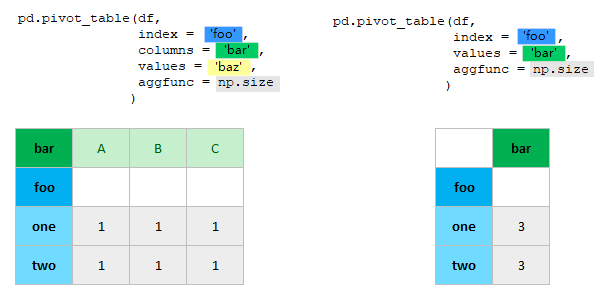
| pivot_table | Create a spreadsheet-style pivot table as a DataFrame. | pd.pivot_table(df, values='D', index=[‘A', ‘B'], columns=[‘C'], aggfunc=np.sum) |
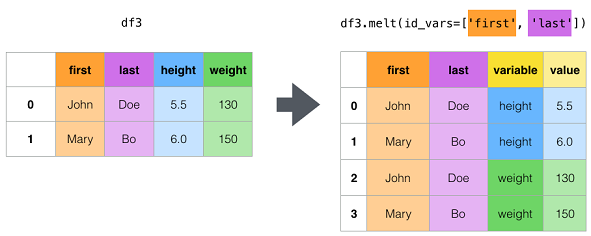
| melt | Unpivot a DataFrame from wide to long format, optionally leaving identifiers set. | df.melt(id_vars=[‘A'], value_vars=[‘B', ‘C']) |
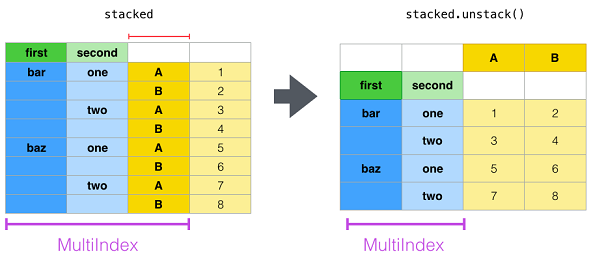
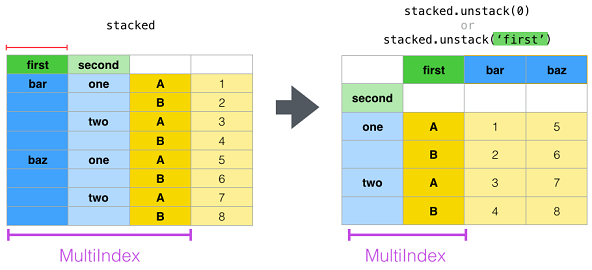
| unstack | Pivot a level of the (necessarily hierarchical) index labels. | df.unstack() |
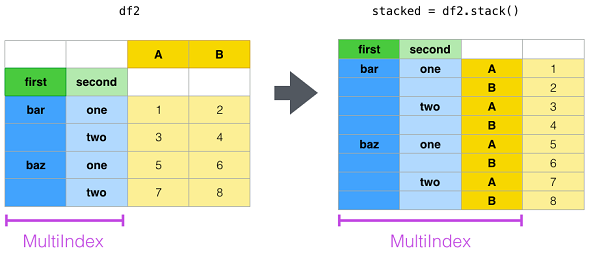
| stack | Stack the prescribed level(s) from columns to index. | df.stack() |
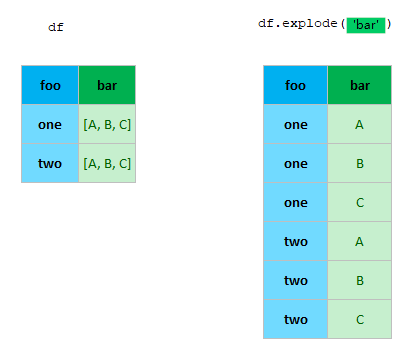
| explode | Transform each element of a list-like to a row, replicating index values. | df.explode(‘A') |
█ pivot and pivot_table
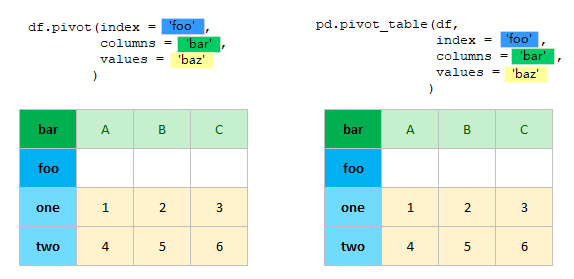
- pivot does not do data aggregation such as min/max/mean
- pivot_table does data aggregation; when aggregation part is left empty in pivot_table, it is same as pivot
pivot
pivot and pivot_table: same results
pivot_table with aggregation
█ melt
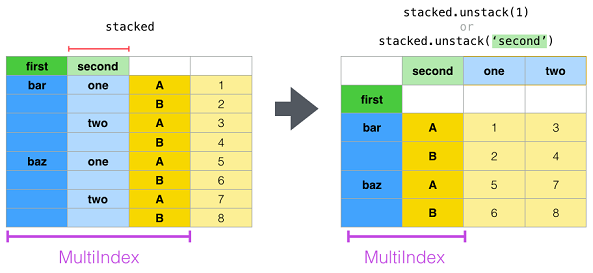
█ stack and unstack
█ explode